Let us create a simple Flutter application to understand the basics of a flutter application in the Android Studio.
Step 1 − Open Android Studio
Step 2 − Create Flutter Project. click File → New → New Flutter Project like below image
Step 3 − Select Flutter Application and click Next.
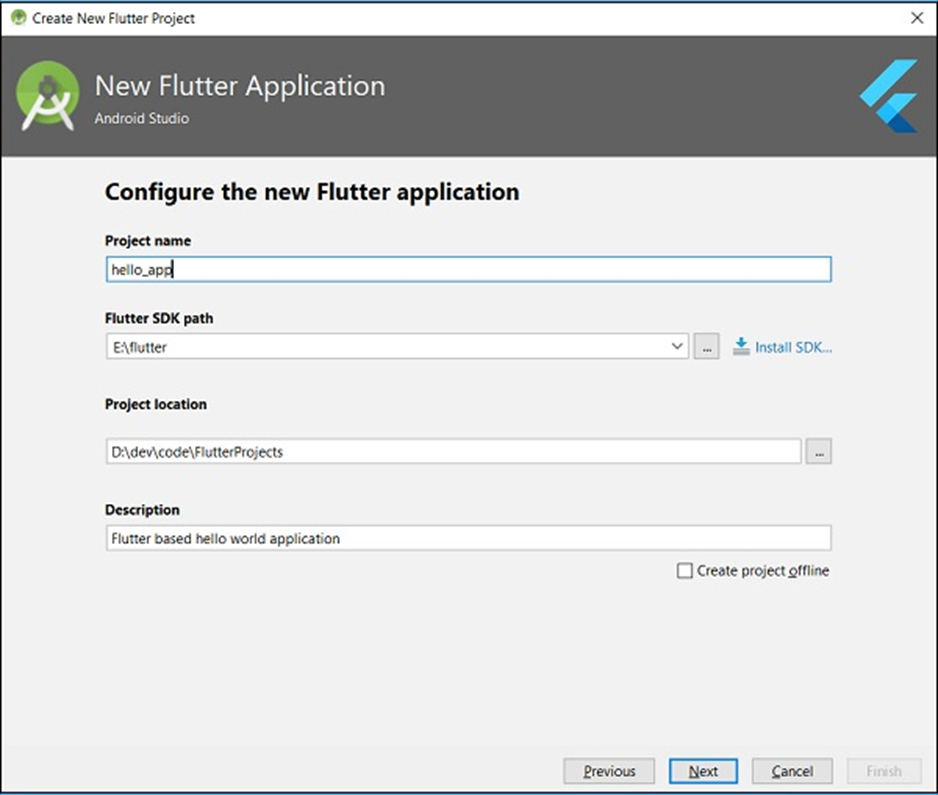
· Project name: hello_app
· Flutter SDK Path: <path_to_flutter_sdk>
· Project Location (Workspace location): <path_to_project_folder>
· Description: App discription
Set the company domain as flutterapp.androindian.com and click Finish.
Step 6 − Enter Company domain.
Android Studio creates a fully working flutter application with minimal functionality. Let us check the structure of the application.
The structure of the application is as follows −
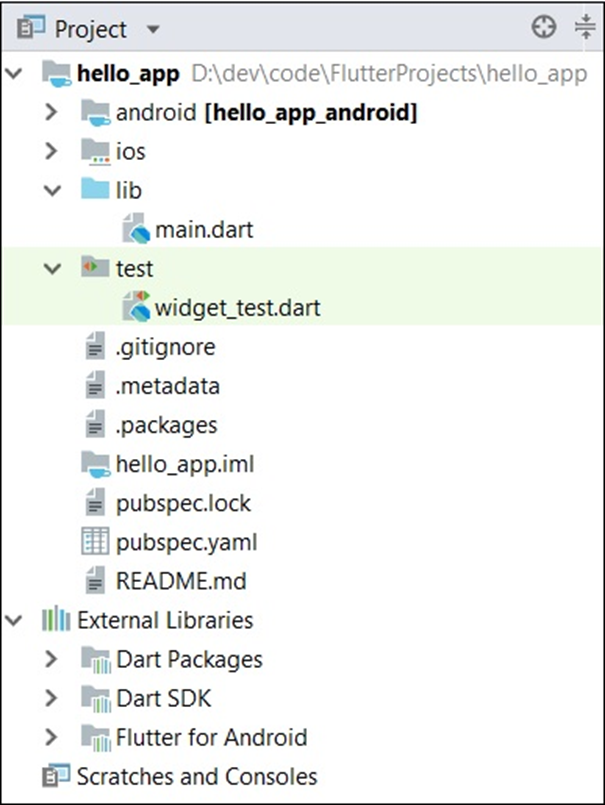
Various components of the application structure −
- android − Auto generated source code for android application
- ios − Auto generated source code for ios application
- lib − Main folder containing Dart code written by flutter framework
- ib/main.dart − Entry point of the Flutter application
- test − Folder containing Dart code to test the flutter application
- test/widget_test.dart − Sample code
- .gitignore − Git version control
- .metadata − auto generated by the flutter framework
- .packages − auto generated to track the flutter packages
- .iml − project file used by Android studio
- pubspec.yaml − Used by Pub (Flutter package manager)
- pubspec.lock − Auto generated by the Flutter package manager, Pub
- README.md − Project description file written in Markdown format
Step 7 − Replace the dart code in the lib/main.dart with the below code −
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Hello World Demo Application',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Home page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(this.title),
),
body: Center(
child:
Text(
'Hello World',
)
),
);
}
}
Let us understand the dart code line by line.
- Line 1 − imports the flutter package(material). The material is a flutter package to create user UI according to the Material design guidelines.
- Line 3 − This is the entry point of the Flutter application. ‘runApp’ function and pass it an object of MyApp class.
- Line 5-17 − Widget is used to create interface in flutter framework. StatelessWidget is a widget, which does not maintain any state of the widget. MyApp extends StatelessWidget and overrides its build method. The purpose of the build method is to create a part of the UI of the app. Here, build method uses MaterialApp, a widget to create the root level UI of the app. It has three properties – title, theme and home.
- title is the title of the app
- theme is the theme of the widget. Here, we set blue as the overall color of the app using ThemeData class and its property, primarySwatch.
- home is the inner UI of the app, which we set another widget, MyHomePage
- Line 19 – 38 − MyHomePage is same as MyApp except it returns Scaffold Widget. Scaffold is a top level of widget next to MaterialApp widget used to create interface conforming material design. It has two important properties, appBar to show the header of the app and body to show the actual content of the app. AppBar is another widget to render the header of the app and we have used it in appBar property. In body property, we have used Center widget, which centers it child widget. Text is the final and inner most widget to show the text and it is displayed in the center of the screen.
Step 8 − Now, run the application using, Run → Run main.dart